Can Ultrasound Detect Cancer?
May 23, 2025
When most people hear the word ultrasound, they picture pregnancy checkups. But did you know this imaging tool also plays a key role in detecting cancer? It’s not just for baby bumps—it’s a powerful, non-invasive technology used across the medical world. Let’s break down how ultrasound fits into the cancer detection puzzle and how NextGen Diagnostic Imaging makes the most of it.
Understanding Ultrasound Imaging
What Is an Ultrasound?
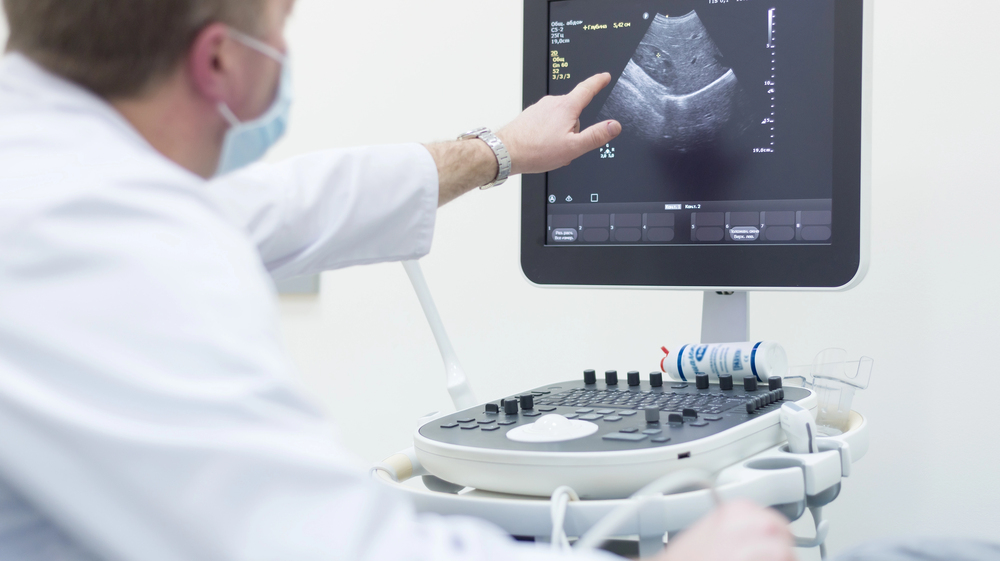
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to capture real-time visuals of internal organs, tissues, and blood flow. It’s widely used in various medical fields, from pregnancy monitoring to tumor detection and organ assessment.
Think of it like sonar technology used by submarines—the machine sends sound waves into the body, and those waves bounce back when they hit something. The machine then reads those echoes and turns them into moving images that doctors can see instantly on a screen. Pretty amazing, right?
Ultrasound is popular because it’s safe, doesn’t use radiation, and gives immediate results, making it ideal for urgent evaluations or guided procedures like biopsies.
How Does It Work?
Here’s the behind-the-scenes magic of an ultrasound:
- A clear, water-based gel is applied to the area of your body being examined. This gel helps eliminate air pockets between the skin and the probe, allowing sound waves to travel efficiently.
- A handheld device called a transducer is then gently moved over the skin. This transducer emits sound waves that penetrate the body.
- These sound waves bounce off tissues, organs, and structures, sending echoes back to the transducer.
- The machine then converts these echoes into live digital images, displayed in real time.
Some ultrasounds also feature Doppler imaging, which evaluates blood flow in vessels. This can be vital in identifying blockages, tumors, or abnormal blood supply that may suggest cancer or other conditions.
Types of Ultrasound Scans
Different clinical needs call for different types of ultrasound approaches. Here’s a quick rundown:
- External Ultrasound: This is the most common type. The probe is moved over the skin’s surface—think of the classic baby ultrasound. It’s used to examine abdominal organs, the thyroid, breasts, and more.
- Internal (Transvaginal or Transrectal) Ultrasound: For deeper or more focused imaging, a specially shaped probe is inserted into the vagina or rectum. This allows for clearer views of pelvic organs, such as the uterus, ovaries, or prostate.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): This is a more advanced method where an ultrasound probe is attached to an endoscope and inserted through the mouth or rectum. It helps get detailed images of organs like the esophagus, pancreas, or nearby lymph nodes—often to detect or stage cancer.
- 3D and 4D Ultrasound: These offer three-dimensional views and live motion capture, commonly used in fetal imaging but also helpful in tumor assessment.
- Elastography Ultrasound: This specialized type evaluates tissue stiffness—stiffer tissues can suggest the presence of tumors. It’s gaining popularity in liver cancer screening and breast imaging.
The Role of Ultrasound in Cancer Detection
What Ultrasound Can See—and What It Can’t
Ultrasound is great at spotting abnormalities in soft tissues—like lumps, masses, or fluid collections. It’s particularly helpful for distinguishing solid tumors (which may be cancerous) from fluid-filled cysts (usually not cancerous). However, it doesn’t image bones or areas filled with air well, like the lungs.
Soft Tissue Focus: Tumors and Masses
It’s most useful for imaging soft tissue organs—breasts, liver, ovaries, testicles, thyroid, and lymph nodes. If there’s a suspicious lump or bump, ultrasound is often one of the first tools doctors reach for.
Real-Time Imaging Advantages
One of ultrasound’s biggest strengths? Real-time imaging. It lets doctors observe movement—like blood flow or the elasticity of a mass—which can help differentiate benign from potentially cancerous growths.
Types of Cancers Ultrasound Can Help Detect
Breast Cancer
Ultrasound is commonly used alongside mammograms to evaluate breast lumps. It’s especially helpful for women with dense breast tissue, where mammograms may not be as clear.
Ultrasound vs. Mammogram
While mammograms are the gold standard for breast cancer screening, ultrasounds offer added detail. Mammograms catch suspicious calcifications; ultrasound shows if that lump is solid or a harmless cyst.
Liver Cancer
Liver ultrasounds help identify abnormal growths, especially in patients with liver disease or those at higher risk. It’s often the first imaging tool used when liver enzymes are elevated.
Ovarian and Uterine Cancers
For pelvic symptoms like bloating or irregular bleeding, transvaginal ultrasound provides clear imaging of ovaries and the uterus. It helps identify masses and abnormal thickening that could signal cancer.
Testicular Cancer
Ultrasound is the go-to method for evaluating testicular lumps. It can quickly determine if a mass is solid (more likely to be cancerous) or cystic (usually benign).
Thyroid Cancer
Neck lumps? An ultrasound can image the thyroid and nearby lymph nodes to check for suspicious nodules. If something looks off, it may lead to a biopsy for further testing.
When Ultrasound Isn’t Enough
Limitations of Ultrasound in Cancer Diagnosis
Here’s the truth: ultrasound isn’t a one-stop solution. It can detect suspicious masses, but it can’t confirm if a tumor is cancerous. That’s where additional tests come in.
Why It’s Often Paired with Other Tests
Ultrasound results often lead to further evaluation—like MRI, CT scans, or biopsies. These tests offer deeper insights, helping confirm whether that mass is malignant.
Why Choose NextGen Diagnostic Imaging?
Expert Radiologists & Advanced Technology
At NextGen Diagnostic Imaging, we combine skilled radiologists with cutting-edge ultrasound equipment. You’re not just getting an image—you’re getting expert eyes that know what to look for.
Patient-First Approach
From start to finish, your comfort and understanding are top priorities. We break things down in plain English, answer your questions, and make the whole process as smooth as possible.
How Ultrasound Fits into a Broader Diagnostic Plan
Biopsy Guidance
Ultrasound is frequently used to guide biopsies. Instead of guessing, doctors use real-time imaging to direct the needle exactly where it needs to go—making biopsies safer and more accurate.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
Ultrasound helps track tumors during and after treatment. Is it shrinking? Staying the same? Growing? This feedback is crucial for adjusting treatment plans in real-time.
Screening vs. Diagnostic Use
Ultrasound isn’t typically used for routine cancer screening (except in certain high-risk patients). But for diagnostic purposes—investigating a new lump or pain—it’s a powerful tool in the early detection process.
Myths About Ultrasound and Cancer
“If It Doesn’t Show on Ultrasound, It’s Not Cancer”
Wrong. Some tumors simply don’t show up well, especially in areas with lots of gas or behind bone. That’s why ultrasound is part of a larger toolkit—not the only tool.
“Ultrasounds Are Only for Pregnancies”
Absolutely not! While they’re famous for baby scans, ultrasounds are used daily in detecting cancer, checking organs, guiding biopsies, and more.
NextGen Diagnostic Imaging Serving the Mahatma Gandhi District Community and Beyond in Houston
NextGen Diagnostic Imaging is dedicated to serving the diverse needs of the local community of Houston, including individuals residing in neighborhoods like Mahatma Gandhi District. With its convenient location near landmarks such as the Draw Academy and major intersections like Windswept Ln. and Westglen Dr. (coordinates: 29.72569691306224, -95.50416586571953), we offer breast ultrasound Houston services.
Get Breast Ultrasound Houston Services at Mahatma Gandhi District Now
Navigate from Mahatma Gandhi District to NextGen Diagnostic Imaging Now
Piecing Together the Bigger Picture
Can ultrasound detect cancer? The short answer: yes—but with limitations. It’s a fantastic tool for spotting suspicious growths in soft tissues and guiding further testing. It won’t diagnose cancer on its own, but it plays a key role in the journey from concern to clarity.
At NextGen Diagnostic Imaging, we bring expertise, care, and the latest technology together to support you every step of the way. When it comes to your health, we believe in combining smart tools with smart people—for the clearest picture possible.
FAQs
1. Is ultrasound painful or risky?
Nope. It’s completely non-invasive, doesn’t involve radiation, and is generally painless—just a bit of cold gel and pressure.
2. How accurate is ultrasound in detecting cancer?
It depends on the location and type of cancer. It’s highly effective in soft tissue areas but less reliable for detecting deeper or hidden tumors.
3. Why would a doctor order an ultrasound after a mammogram?
To get a closer look at a specific area—especially if the breast tissue is dense or a lump needs more detailed imaging.
4. Can ultrasound be used during cancer treatment?
Yes! It’s often used to monitor tumor response to treatment and help guide biopsies or fluid drainage procedures.
5. Is ultrasound used in emergency cancer detection?
Sometimes, yes. In ER settings, it’s a fast way to assess organs and detect large tumors or internal bleeding that could relate to undiagnosed cancers.

NextGen Scan
Contact Us: We’re Here to Help!
We’d love to hear from you! Whether you have questions about our services, need more information on our diagnostic and pain management options, or would like to schedule an appointment, our friendly and professional team is here to assist you every step of the way. We are dedicated to providing you with the best care and support, and we are happy to address any concerns or inquiries you may have.